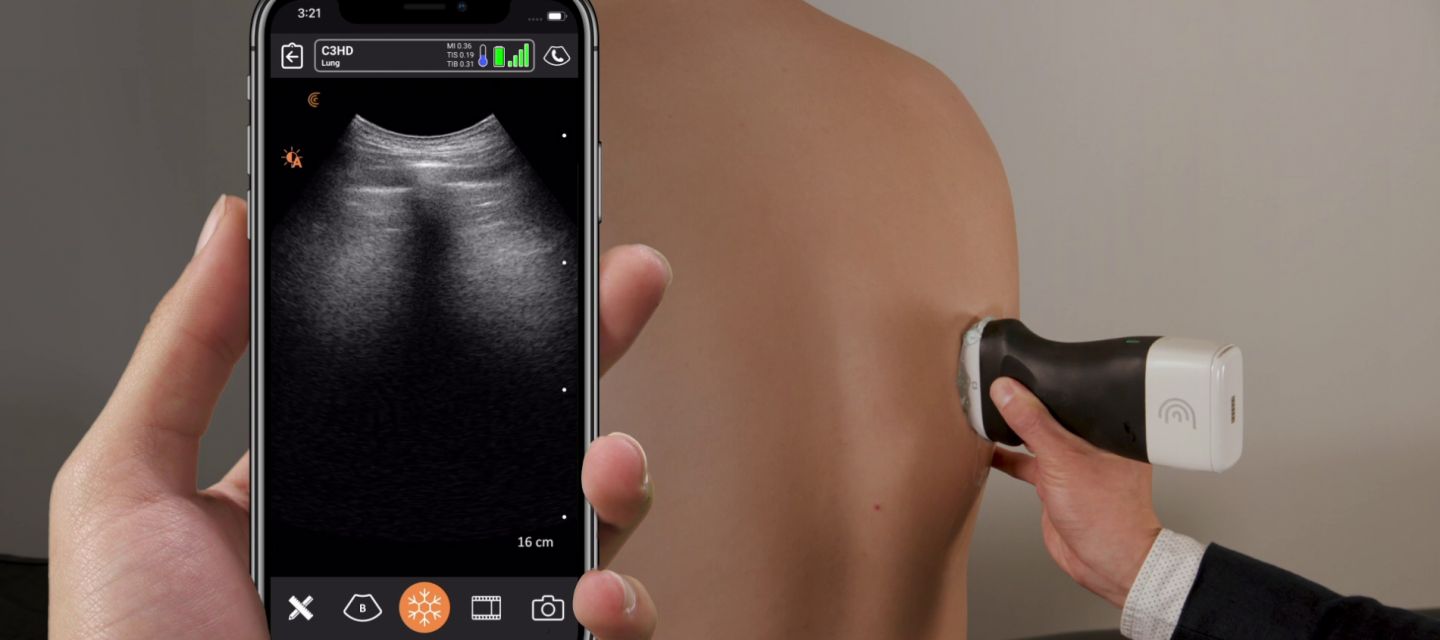
Scanner expected to speed up diagnoses in rural and remote areas
UBC researchers are collaborating with local partners to establish a network of portable, handheld ultrasound scanners that can soon accelerate COVID-19 diagnosis in B.C. and potentially beyond.
The scanners pair a locally developed ultrasound device with a secure online library of lung ultrasound images and a specially developed artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm, allowing health care practitioners to diagnose COVID-19 at the point of care—almost instantly.
Family doctors and acute care units in rural B.C. will be the first users, with 50 units ready for deployment. More than 30 additional scanners will be distributed to urban acute care sites managed by Vancouver Coastal Health.
The project is co-led by Dr. Oron Frenkel, an emergency physician at St. Paul’s Hospital and a clinical assistant professor at UBC’s faculty of medicine; Dr. Teresa Tsang, UBC cardiologist and professor of medicine and director of echocardiography at Vancouver General Hospital and UBC Hospital; Purang Abolmaesumi, professor of electrical and computer engineering; and Robert Rohling, professor of electrical and computer engineering and mechanical engineering.

“With this scanner, we can potentially detect COVID-19 lung changes earlier while waiting for lab test results,” says Tsang. “This may also enable us to anticipate who will likely deteriorate rapidly, so that we can support these patients optimally from the start.”
Data from the field suggests that the scanner can detect up to 33 per cent more cases of COVID-19 pneumonia than some current lab tests. “It’s easy to use, so even physicians with less experience can obtain fast, accurate results,” said Tsang.
The team will build Canada’s first ultrasound library for lung disease and will use AI to enable the handheld scanners to accurately detect patterns typical of COVID-19 and other lung diseases at the point of care.
“This project demonstrates UBC’s expertise in applied AI research,” said Purang Abolmaesumi, the Canada Research Chair in Biomedical Engineering at UBC. “With these scanners, we showcase UBC’s and B.C.’s cutting-edge capabilities in developing AI technology for medical imaging, with direct impact on our community and the Canadian health care system.”

Robert Rohling, who also leads the Institute for Computing, Information and Cognitive Systems at UBC, highlighted the different contributions of the project members and partners. “Providing accurate, timely diagnostics for COVID-19 is a tremendous challenge. What really helps to solve it is the diverse and talented team. Each member is a leader in their field but more important is that doctors are working with engineers and UBC is working with B.C. companies.”
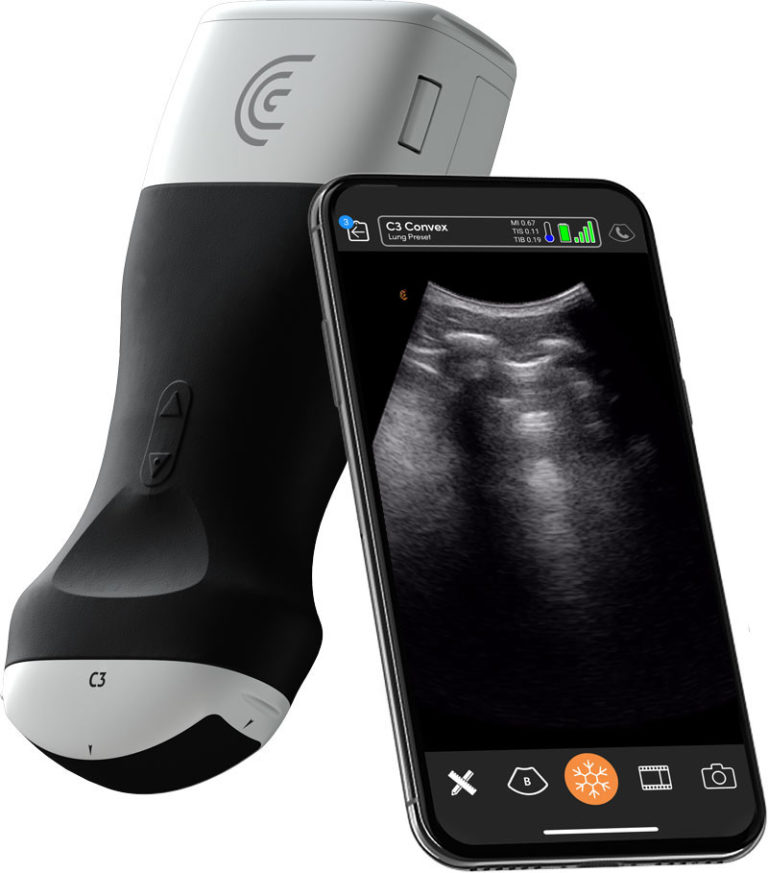
The scanners can be used for point-of-care ultrasound (commonly abbreviated PoCUS), and were designed and provided by Burnaby-based Clarius Mobile Health. They can be disinfected easily between patients and come with a mobile phone app for ease of use.
Pivoting in the midst of COVID-19
The Clarius scanners have been in use since 2017 but were swiftly adapted in March to diagnose COVID-19 in order to contribute to the public health response to the virus.
It is part of Intelligent Network Point of Care Ultrasound (IN-PoCUS), a $2.5 million project led by B.C.’s Digital Technology Supercluster aimed at improving health care diagnosis in rural B.C.
The Digital Technology Supercluster solves some of industry’s and society’s biggest problems through Canadian-made technologies. It brings together private and public sector organizations of all sizes to address challenges facing Canada’s economic sectors including healthcare, natural resources, manufacturing and transportation.
Other funding and in-kind contributions were provided by Providence Health Care, Clarius Mobile Health, Change Healthcare, UBC, Vancouver Coast Health and Rural Coordination Centre BC.